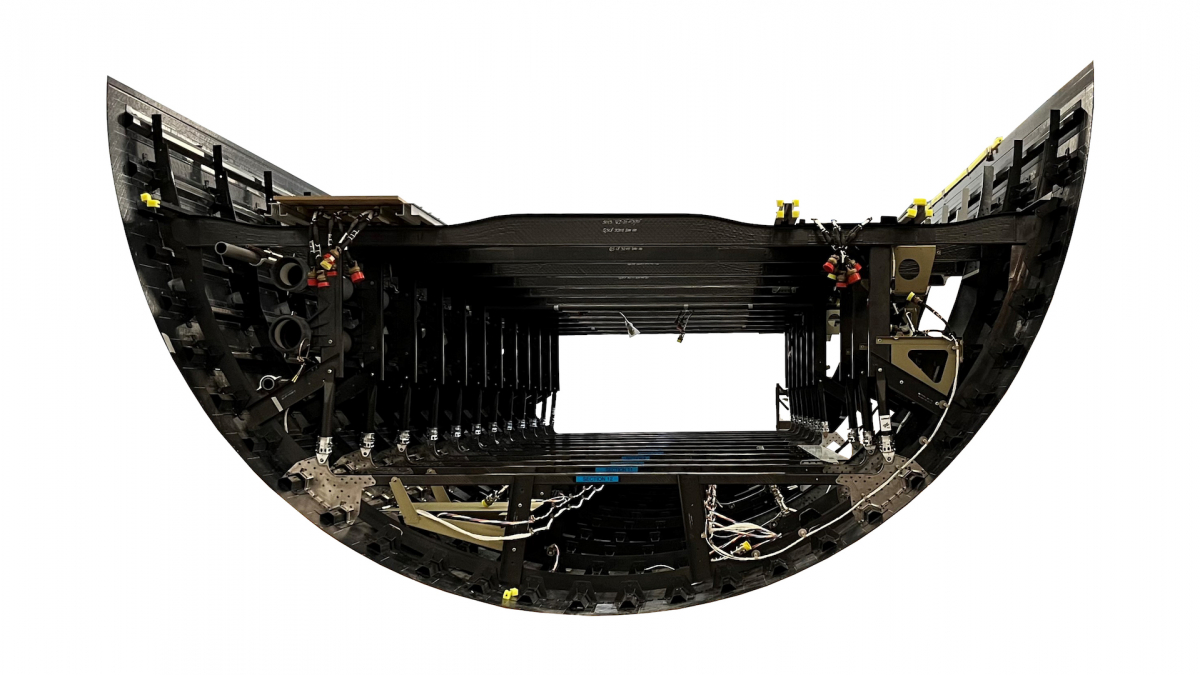
GKN Fokker, NLR - Netherlands Aerospace Centre, Delft University of Technology and SAM|XL, have successfully manufactured one the world’s largest thermoplastic components as part of the Multi-Functional Fuselage Demonstrator (MFFD) project led by Airbus.
The 8m by 4m composite structure will act as the lower half of the fuselage demonstrator.
GKN Fokker, NLR-Netherlands Centre, Delft University of Technology and SAMIXL have successfully manufactured one the world’s largest thermoplastic components as part of the Multi-Functional Fuselage Demonstrator (MFFD) project led by Airbus. This demonstrates how the use of thermoplastic composites can help realize a next-gen fleet of aircraft capable of offering the same strength and durability as aluminum, while drastically reducing the fuselage recurring cost, as well as the overall weight of aircraft and the subsequent emissions. The 8m by 4m composite structure - delivered under the Clean Sky 2 STUNNING project - will act as the lower half of the fuselage demonstrator.
To demonstrate High Rate Production of a minimum of 60 aircraft per month
The ground-breaking aerostructure consists of more than 400 thermoplastic fibre-reinforced parts, as well as thousands of spot welds and hundreds of meters of continuous welds. The fuselage lower half will be joined at Fraunhofer IFAM in Stade with the upper half made by German Aerospace Center (DLR) Institute of Structures and Design in Augsburg. The MFFD project aims to demonstrate High Rate Production (HRP) of a minimum of 60 aircraft per month (up to 100 aircraft), reduce the total fuselage weight by 1 ton (10%), and reduce the total fuselage recurring cost by €1m (20%). STUNNING contributed to these objectives by showcasing novel thermoplastic manufacturing and joining technologies, as well as modular manufacturing techniques and automation.
GKN Fokker was responsible for the assembly of STUNNING, which consisted of a skin module and a floor grid module
GKN Fokker was responsible for the assembly of STUNNING, which consisted of a skin module and a floor grid module. The skin module featured a skin made as a single part by NLR using Automatic Fiber Placement, 38 stringers from Xelis made using continuous compression moulding, some of which joggled by NLR, 208 injection-moulded clips produced by the ECO-CLIP consortium, and frame sub-assemblies. The floor grid module included floor beam sub-assemblies with passenger floor beams made by automatic fibre placement. Both frame and floor beam sub-assemblies were made by GKN Fokker. The floor grid was fully equipped with various systems before installation in the skin module.
Potential for industrial-scale application of robotic welding in the assembly of thermoplastic aerostructures
Arnt Offfringa, Director Global Technology Center NL of GKN Aerospace said: “This breakthrough project, which began in 2017, has significantly advanced our understanding and accelerated the development of thermoplastic technologies for large and complex aircraft parts. It has showcased the potential for industrial-scale application of robotic welding in the assembly of thermoplastic aerostructures. The partnership approach to STUNNING has also been a great success, showing how much progress can be made when working together. Collaboration projects such as this will be vital as we continue to push the boundaries of technology in order to meet our sustainability targets.”
The demonstrator was assembled in SAM|XL at the TU Delft Campus
The demonstrator was assembled in SAM|XL at the TU Delft Campus, where a 10x11x4m ultrasonic welding robot was built from numerous machine parts and software components supplied by European partners. Team SAM|XL was responsible for the integration of the robotic welding cell and the development of smart control and programming methods. Valuable lessons were learned related to ‘design for automated assembly’. In a joint effort, rapid energy-efficient ultrasonic welding technology was scaled-up from the lab at the Faculty of Aerospace Engineering to an industrial-scale solution for dust-less assembly of the demonstrator involving 1600 structurally sound spot welds. Further maturation of this game changing assembly technology will be accelerated in SAM|XL’s new robotic welding lab.